基于Netty的Spring Boot内置Servlet容器的实现(三)
EmbeddedServletContainer实现
Spring Boot启动过程与EmbeddedServletContainer
一般来说,Spring Boot的应用如果使用内置Servlet容器单独运行,我们都会在main()方法中调用
SpringApplication.run(Object source, String... args);
方法。通过source参数构造一个SpringApplication对象再调用其
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args);
方法,这个方法先通过createApplicationContext()创建一个AnnotationConfigEmbeddedWebApplicationContext对象,随后会调用到
protected void refresh(ApplicationContext applicationContext);
方法,这个方法会调用到AbstractApplicationContext的refresh()方法。而通过下面的UML图可以看到,AnnotationConfigEmbeddedWebApplicationContext是AbstractApplicationContext的子类。
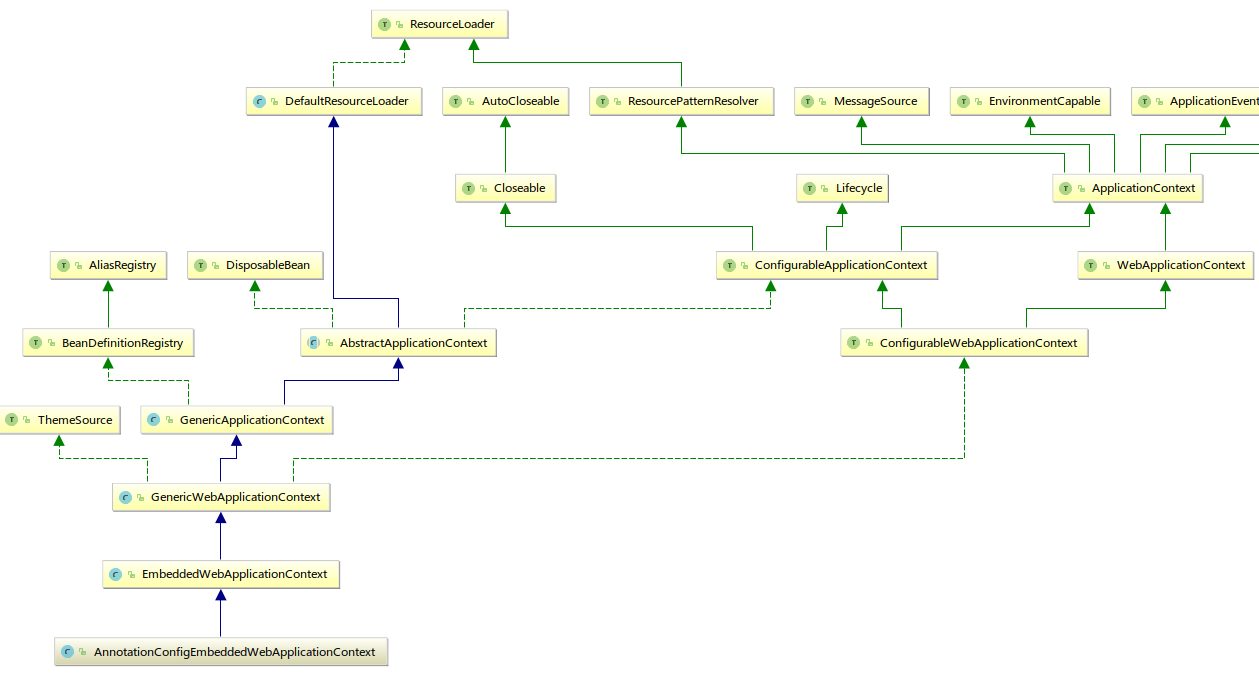 实际上,这里使用了模板设计模式,
实际上,这里使用了模板设计模式,refresh()的具体流程由父类AbstractApplicationContext定义,具体的一些操作由子类去实现,在子类调用refresh()方法的时候,调用的是子类实现的操作方法,如:
protected void onRefresh() throws BeansException
方法。这个方法在AnnotationConfigEmbeddedWebApplicationContext的父类EmbeddedWebApplicationContext中有实现:
protected void onRefresh() {
super.onRefresh();
try {
this.createEmbeddedServletContainer();
} catch (Throwable var2) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start embedded container", var2);
}
}
private void createEmbeddedServletContainer() {
EmbeddedServletContainer localContainer = this.embeddedServletContainer;
ServletContext localServletContext = this.getServletContext();
if (localContainer == null && localServletContext == null) {
EmbeddedServletContainerFactory containerFactory = this.getEmbeddedServletContainerFactory();
this.embeddedServletContainer = containerFactory.getEmbeddedServletContainer(new ServletContextInitializer[]{this.getSelfInitializer()});
} else if (localServletContext != null) {
try {
this.getSelfInitializer().onStartup(localServletContext);
} catch (ServletException var4) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Cannot initialize servlet context", var4);
}
}
this.initPropertySources();
}
检查embeddedServletContainer私有变量是否为空,为空的话获取EmbeddedServletContainerFactory工厂类(就是我们写的EmbeddedNettyFactory),获取到EmbeddedServletContainer实例并赋值给this.embeddedServletContainer。
在模板方法AbstractApplicationContext.refresh()中,调用onRefresh()后,会继续调用finishRefresh(),通过上面的分析我们知道实际调用的是EmbeddedWebApplicationContext.finishRefresh():
protected void finishRefresh() {
super.finishRefresh();
EmbeddedServletContainer localContainer = this.startEmbeddedServletContainer();
if (localContainer != null) {
this.publishEvent(new EmbeddedServletContainerInitializedEvent(this, localContainer));
}
}
private EmbeddedServletContainer startEmbeddedServletContainer() {
EmbeddedServletContainer localContainer = this.embeddedServletContainer;
if (localContainer != null) {
localContainer.start();
}
return localContainer;
}
可以看到他调用了私有方法startEmbeddedServletContainer()启动容器,在这个方法里面,获取this.embeddedServletContainer(就是我们本文要实现的NettyContainer)然后执行其start()方法,以启动内置Servlet容器。
因此我们应该在EmbeddedServletContainer实现类的start()对Netty服务器进行初始化。
NettyContainer
自己编写的内置Servlet容器需要实现EmbeddedServletContainer接口,具体包括以下三个方法:
public interface EmbeddedServletContainer {
void start() throws EmbeddedServletContainerException; //Spring Boot启动时调用
void stop() throws EmbeddedServletContainerException; //Spring Boot关闭时调用
int getPort(); //获取端口
}
这几个方法的用途比较清晰明确了,接下来就是实现。
构造方法
首先在之前写的EmbeddedNettyFactory工厂类里面,需要调用将要写的EmbeddedNettyFactory的构造方法,并将必要的参数传入其构造方法,比如端口号、以及已经i初始化完毕的ServletContext实例。
构造方法:
private final InetSocketAddress address; //监听端口地址
private final NettyContext context; //Context
public NettyContainer(InetSocketAddress address, NettyContext context) {
this.address = address;
this.context = context;
}
在EmbeddedNettyFactory中修改为:
public EmbeddedServletContainer getEmbeddedServletContainer(ServletContextInitializer... initializers) {
/*…………………………*/
//return null;
return new NettyContainer(address, context); //初始化容器并返回
}
@Override
public int getPort() {
return address.getPort();
}
start()
通过以上的分析,我们知道EmbeddedServletContainer的start()是由AbstractApplicationContext.refresh()模板方法负责调用启动的,我们应该在这个方法里面初始化Netty服务器。Netty的启动大家应该比较清楚了,无非就是设置两个EventLoopGroup用于处理请求的获取与读写,并设置Pipeline上的Handler,最后绑定端口,启动服务。以下是具体实现的代码:
@Override
public void start() throws EmbeddedServletContainerException {
servletContext.setInitialised(false);
ServerBootstrap sb = new ServerBootstrap();
//根据不同系统初始化对应的EventLoopGroup
if ("Linux".equals(StandardSystemProperty.OS_NAME.value())) {
bossGroup = new EpollEventLoopGroup(1);
workerGroup = new EpollEventLoopGroup();//不带参数,线程数传入0,实际解析为 Math.max(1, SystemPropertyUtil.getInt("io.netty.eventLoopThreads", Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() * 2));
sb.channel(EpollServerSocketChannel.class)
.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.option(EpollChannelOption.TCP_CORK, true);
} else {
bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
sb.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.group(bossGroup, workerGroup);
}
sb.option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_REUSEADDR, true)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 100);
log.info("Bootstrap configuration: " + sb.toString());
servletExecutor = new DefaultEventExecutorGroup(50);
sb.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline p = ch.pipeline();
p.addLast("codec", new HttpServerCodec(4096, 8192, 8192, false)); //HTTP编码解码Handler
p.addLast("servletInput", new ServletContentHandler(servletContext)); //处理请求,读入数据,生成Request和Response对象
p.addLast(checkNotNull(servletExecutor), "filterChain", new RequestDispatcherHandler(servletContext)); //获取请求分发器,让对应的Servlet处理请求,同时处理404情况
}
});
servletContext.setInitialised(true);
ChannelFuture future = sb.bind(address).awaitUninterruptibly();
Throwable cause = future.cause();
if (null != cause) {
throw new EmbeddedServletContainerException("Could not start Netty server", cause);
}
log.info(servletContext.getServerInfo() + " started on port: " + getPort());
}
这里有两个Handler类是我们实现的——ServletContentHandler和RequestDispatcherHandler,我们将在后面讲解。
stop()
在stop()方法里应该关闭在start()方法中开启的资源,以便Spring Boot关闭,防止资源/内存泄漏:
@Override
public void stop() throws EmbeddedServletContainerException {
try {
if (null != bossGroup) {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully().await();
}
if (null != workerGroup) {
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully().await();
}
if (null != servletExecutor) {
servletExecutor.shutdownGracefully().await();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new EmbeddedServletContainerException("Container stop interrupted", e);
}
}
Netty服务设计
设计思路
看过Tomcat之类Servlet容器的源码的话,应该对Servleti容器设计有一点概念。
- 首先我们需要通过Socket,处理HTTP连接,获取请求的数据,这一块可通过netty的API进行。
- 然后对接收到的数据进行解析封装成
HttpServletRequest和HttpServletResponse对象,这一块需要netty自带的http解码编码器,并自定义Handler来i实现。 - 而
HttpServletRequest本身也需要一些处理,比如Cookie、Session、Attributes(懒解析),需要自行实现。 - 接着需要对请求路径进行匹配,找到对应处理的Servlet, 这一部分前面已经实现了(2017-08-26似乎还有点Bug需要解决)。
- 接下来就是调用对应Servlet的
service()方法,等待返回(在容器启动的时候需要对有on-startup的Servlet进行init()方法的调用)。 - Servlet返回后,包装响应,处理异常和HTTP错误。
- HTTP编码响应返回。
- 容器关闭的时候,调用所有已注册的Servlet的
destroy()方法,并关闭打开的资源。
自定义Netty的Handler处理请求响应
根据前面的分析,我们的netty服务需要三个Handler,其中HTTP解码编码的有现成的HttpServerCodec,另外两个则需要我们自己实现。
首先是对请求进行封装的Handler, 功能:
- channel激活时, 开启一个新的输入流
- 有信息/请求进入时,封装请求和响应对象,执行读操作
- channel恢复时,关闭输入流,等待下一次连接到来
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
inputStream = new HttpRequestInputStream(ctx.channel());
}
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
if (msg instanceof HttpRequest) {
HttpRequest request = (HttpRequest) msg;
HttpResponse response = new DefaultHttpResponse(HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1, HttpResponseStatus.OK, false);
HttpUtil.setKeepAlive(response, HttpUtil.isKeepAlive(request));
NettyHttpServletResponse servletResponse = new NettyHttpServletResponse(ctx, servletContext, response);
NettyHttpServletRequest servletRequest = new NettyHttpServletRequest(ctx, servletContext, request, servletResponse, inputStream);
if (HttpUtil.is100ContinueExpected(request)) { //请求头包含Expect: 100-continue
ctx.write(new DefaultFullHttpResponse(HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1, HttpResponseStatus.CONTINUE), ctx.voidPromise());
}
ctx.fireChannelRead(servletRequest);
}
if (msg instanceof HttpContent) {
inputStream.addContent((HttpContent) msg);
}
}
@Override
public void channelInactive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
inputStream.close();
}
然后是一个处理URL匹配分发请求的Handler,完成以下功能:
- 读入请求数据时,对请求URI获取分发器
- 找不到返回404错误.
- 找到则调用FilterChain进行业务逻辑
- 最后关闭输出流
@Override
public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ctx.flush();
}
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, NettyHttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
HttpServletResponse servletResponse = (HttpServletResponse) request.getServletResponse();
try {
NettyRequestDispatcher dispatcher = (NettyRequestDispatcher) context.getRequestDispatcher(request.getRequestURI());
if (dispatcher == null) {
servletResponse.sendError(404);
return;
}
dispatcher.dispatch(request, servletResponse);
} finally {
if (!request.isAsyncStarted()) {
servletResponse.getOutputStream().close();
}
}
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
logger.error("Unexpected exception caught during request", cause);
ctx.close();
}
