使用Thymeleaf模板引擎
Thymeleaf简介
Thymeleaf是一个XML/XHTML/HTML5模板引擎,可用于Web与非Web环境中的应用开发。它是一个开源的Java库,基于Apache License 2.0许可。
Thymeleaf提供了一个用于整合Spring MVC的可选模块,在应用开发中,你可以使用Thymeleaf来完全代替JSP或其他模板引擎,如Velocity、FreeMarker等。Thymeleaf的主要目标在于提供一种可被浏览器正确显示的、格式良好的模板创建方式,因此也可以用作静态建模 。你可以使用它创建经过验证的XML与HTML模板。相对于编写逻辑或代码,开发者只需将标签属性添加到模板中即可。
Thymeleaf主要通过HTML的标签属性渲染标签内容,浏览器在解析html时,当检查到Thymeleaf的属性时候会忽略,所以Thymeleaf的模板可以通过浏览器直接打开展现,这样非常有利于前后端的分离 。
添加依赖
添加模板引擎的依赖,可以在IntelliJ IDEA创建Spring Boot项目的时候选择对应的依赖,也可以在后期手动修改pom.xml文件增加依赖。
IntelliJ IDEA创建Spring Boot项目时增加
在选择依赖的界面,点击左边的“Template Engine”,在中间选择所需的模板引擎即可。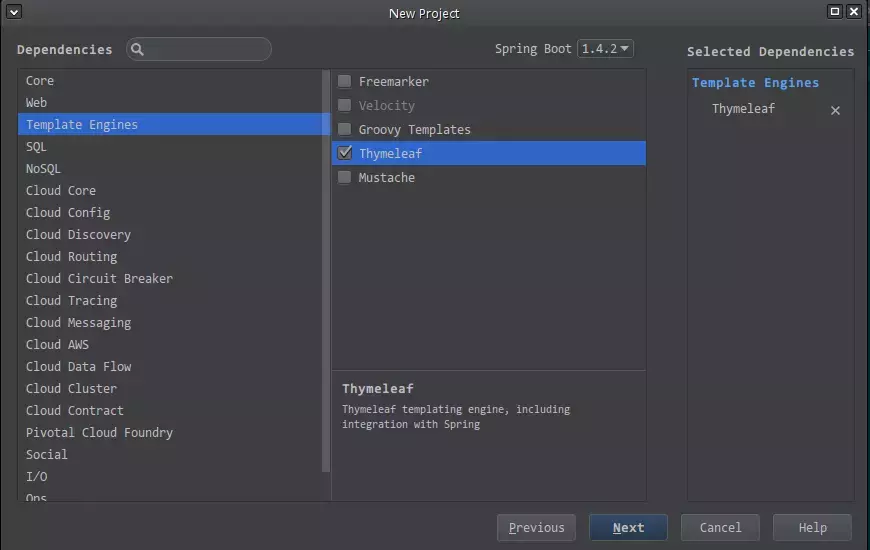
手动修改pom.xml
以Thymeleaf为例,修改pom.xml增加以下依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
可在resources/application.properties中对Thymeleaf进行配置。
目录结构
Thymeleaf默认将模板放在resources/templates目录下(可以通过application.properties文件进行配置,但建议保持默认值方便管理);同时,Spring Boot默认将静态资源放在resources/static(从根路径访问),于是,经典的目录结构是这样的: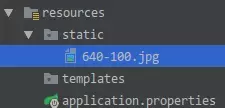
其中640-100.jpg的访问路径为http://127.0.0.1:8080/640-100.jpg。
模板Demo
在resources/templates目录下新建temp.html,内容如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head lang="en">
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<h1 th:text="${host}">Hello World</h1>
</body>
</html>
其中h1的th:text="${host}" 即为Thymeleaf的属性,表示获取ModelMap中的host属性赋值给h1的文本;而这个文件直接用浏览器访问的时候h1元素则显示“Hello World”。 再编写一个Controller:
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/template")
public class TemplateController {
@RequestMapping("/")
public String index(ModelMap map) {
// 加入一个属性,用来在模板中读取
map.addAttribute("host", "http://www.turingdi.com");
// return模板文件的名称,对应resources/templates/temp.html
return "temp";
}
}
注意这里使用了@Controller注解而不是之前的@RestController,若使用后者,index()方法返回的”temp”会直接以JSON格式返回,页面显示“temp”。实际上我们使用@Controller注解并加入了Thymeleaf模板引擎后,index()方法返回的”temp”会被Thymeleaf模板引擎理解为src/main/resources/templates/temp.html文件,然后解析该文档并响应返回。在浏览器中接收到的html源码如下: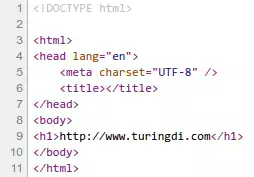
而这个模板文件直接用浏览器打开的效果: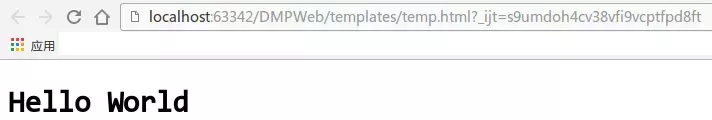
可以看到,前端开发人员可以直接修改html并直接观察修改后的效果,修改时并不影响Thymeleaf的代码,因此可以方便前后端协同开发。
Thymeleaf简单表达式
变量表达式 ${……}
<input type="text" name="userName" value="James Carrot" th:value="${user.name}" />
上述代码为引用user对象的name属性值。
选择/星号表达式 *{……}
<div th:object="${session.user}">
<p>Nationality:
<span th:text="*{nationality}">Saturn</span>.
</p>
</div>
选择表达式一般跟在th:object后,直接取object中的属性。
文字国际化表达式 #{……}
<p th:utext="#{home.welcome}">Welcome to our grocery store!</p>
URL表达式 @{……}
<a href="details.html" th:href="@{/order/details(orderId=${o.id})}">view</a>
@{……}支持决定路径和相对路径。其中相对路径又支持跨上下文调用url和协议的引用。 当URL为后台传出的参数时,代码如下:
<img src="../../static/assets/images/qr-code.jpg" th:src="@{${path}}" alt="二维码" />
Thymeleaf常用标签
简单数据转换(数字,日期)
<dt>价格</dt>
<dd th:text="${#numbers.formatDecimal(product.price, 1, 2)}">180</dd>
<dt>进货日期</dt>
<dd th:text="${#dates.format(product.availableFrom, 'yyyy-MM-dd')}">2014-12-01</dd>
字符串拼接
<dd th:text="${'$'+product.price}">235</dd>
表单
<form th:action="@{/bb}" th:object="${user}" method="post" th:method="post">
<input type="text" th:field="*{name}"/>
<input type="text" th:field="*{msg}"/>
<input type="submit"/>
</form>
循环
渲染列表数据是一种非常常见的场景,例如现在有n条记录需要渲染成一个表格<table>,该数据集合必须是可以遍历的,使用th:each标签:
<table>
<tr>
<th>NAME</th>
<th>PRICE</th>
<th>IN STOCK</th>
</tr>
<tr th:each="prod : ${prods}">
<td th:text="${prod.name}">Onions</td>
<td th:text="${prod.price}">2.41</td>
<td th:text="${prod.inStock}? #{true} : #{false}">yes</td>
</tr>
</table>
条件判断If/Unless
Thymeleaf中使用th:if和th:unless属性进行条件判断,下面的例子中,<a>标签只有在th:if中条件成立时才显示:
<a th:href="@{/login}" th:unless=${session.user != null}>Login</a>
th:unless于th:if恰好相反,只有表达式中的条件不成立,才会显示其内容。
Switch
Thymeleaf同样支持多路选择Switch结构,默认属性default可以用*表示:
<div th:switch="${user.role}">
<p th:case="'admin'">User is an administrator</p>
<p th:case="#{roles.manager}">User is a manager</p>
<p th:case="*">User is some other thing</p>
</div>
Thymeleaf配置
可在resources/application.properties 中对Thymeleaf进行配置,配置如下:
# Enable template caching.
spring.thymeleaf.cache=true
# Check that the templates location exists.
spring.thymeleaf.check-template-location=true
# Content-Type value.
spring.thymeleaf.content-type=text/html
# Enable MVC Thymeleaf view resolution.
spring.thymeleaf.enabled=true
# Template encoding.
spring.thymeleaf.encoding=UTF-8
# Comma-separated list of view names that should be excluded from resolution.
spring.thymeleaf.excluded-view-names=
# Template mode to be applied to templates. See also StandardTemplateModeHandlers.
spring.thymeleaf.mode=HTML5
# Prefix that gets prepended to view names when building a URL.
spring.thymeleaf.prefix=classpath:/templates/
# Suffix that gets appended to view names when building a URL.
spring.thymeleaf.suffix=.html spring.thymeleaf.template-resolver-order= # Order of the template resolver in the chain. spring.thymeleaf.view-names= # Comma-separated list of view names that can be resolved.